Obesity Alert by PM Narendra Modi: Understanding, Preventing, and Combating Obesity in India
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently raised a crucial alert regarding the increasing obesity rates in India, referencing a concerning projection from The Lancet journal stating that nearly 44 crore Indians could become obese by 2050. Such a development could significantly strain India’s healthcare resources and economic stability, given the strong association between obesity and chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, and certain cancers.
Early Signs of Developing Obesity: Recognizing obesity at an early stage is crucial for effective intervention. Key early signs include:
- Noticeable increase in waist circumference.
- Gradual weight gain despite a consistent diet.
- Increasing fatigue and reduced energy levels.
- Frequent breathlessness during minimal physical activities.
- Joint pain due to additional pressure from excess weight.
Behavioural Trends in Potentially Obese Individuals: People at risk of obesity often display behavioural patterns such as:

- Emotional eating or binge eating triggered by stress or anxiety.
- Preference for sedentary activities like prolonged screen time, including smartphones, computers, and television.
- Regular snacking between meals, especially on processed or high-calorie snacks.
- Low motivation for physical activity or exercise.
Role of Stress:

Stress plays a critical role in obesity development by increasing cortisol levels, a hormone that promotes fat storage, especially around the abdomen. Chronic stress often leads individuals to adopt unhealthy coping mechanisms like overeating, binge eating, or choosing unhealthy comfort foods, significantly contributing to weight gain.
Lifestyle Factors: Modern lifestyle, especially in urban India, significantly contributes to obesity. Factors include:

- Sedentary jobs involving long hours of sitting.
- Easy availability and affordability of fast food and processed snacks.
- Minimal daily physical activity, compounded by reliance on vehicles rather than walking or cycling.
- Social and cultural habits encouraging frequent large gatherings centered around food.
Sleep Habits:

Poor sleep quality and insufficient sleep duration directly correlate with obesity. Lack of sleep disrupts hormonal balance, increasing ghrelin (hunger hormone) and decreasing leptin (satiety hormone), leading to overeating. It also increases cravings for sugary and fatty foods, thus accelerating weight gain.
Eating Habits and the Indian Diet: The traditional Indian diet, although nutritionally rich, can contribute to obesity if consumed incorrectly. Common practices that escalate obesity include:

- High consumption of carbohydrates, particularly refined grains like white rice and bread.
- Excessive use of cooking oil and deep-frying methods.
- Frequent consumption of sweets, desserts, and sugary beverages.
- Limited intake of fresh fruits, vegetables, fiber, and protein-rich foods.
Therapeutic and Preventive Guidance for Indians: Combating obesity requires holistic approaches encompassing dietary adjustments, lifestyle modifications, stress management, and preventive healthcare:
- Dietary Recommendations:
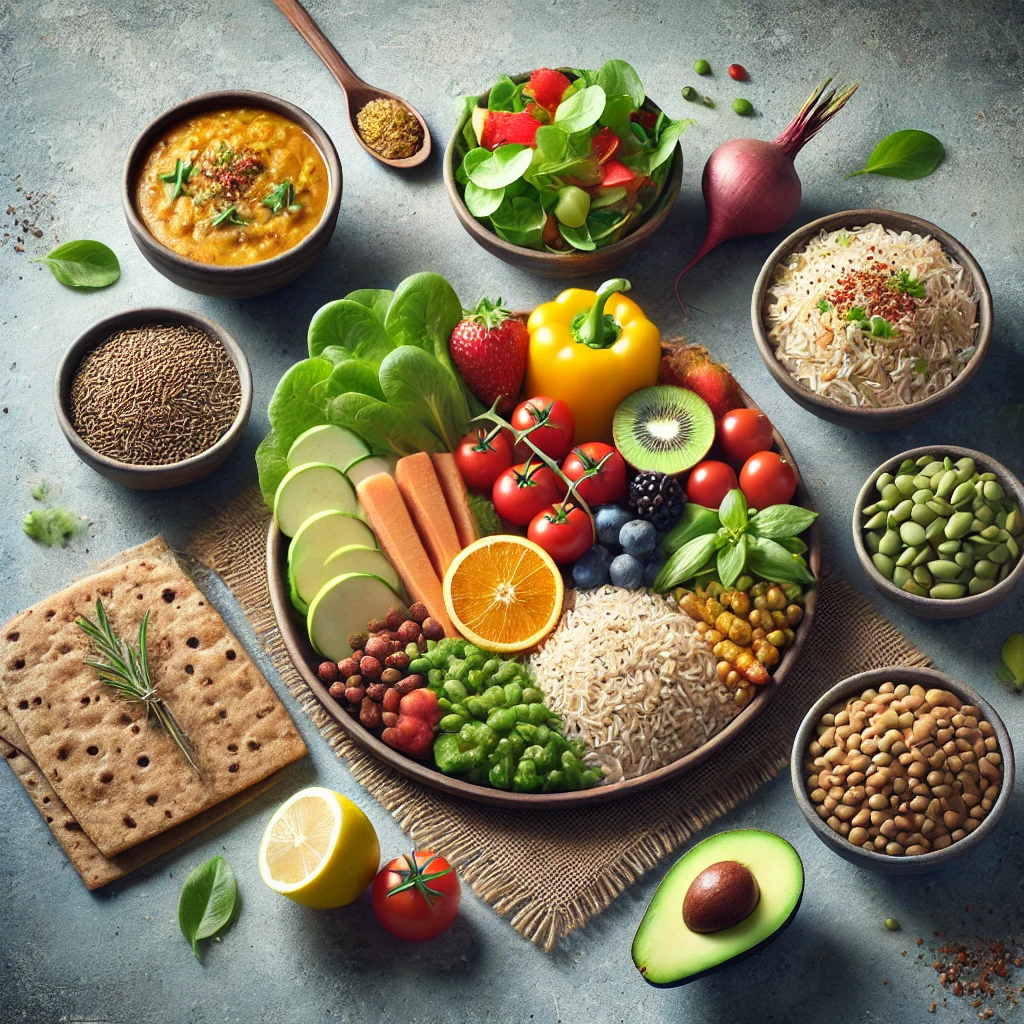

- Limit consumption of refined carbohydrates and switch to whole grains (millets, brown rice, oats).
- Increase intake of fresh fruits and vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
- Reduce the use of cooking oil, opting for healthier options like olive oil, mustard oil, or minimal oil cooking methods such as baking, grilling, steaming, and sautéing.
- Reduce portion sizes and avoid eating late at night.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
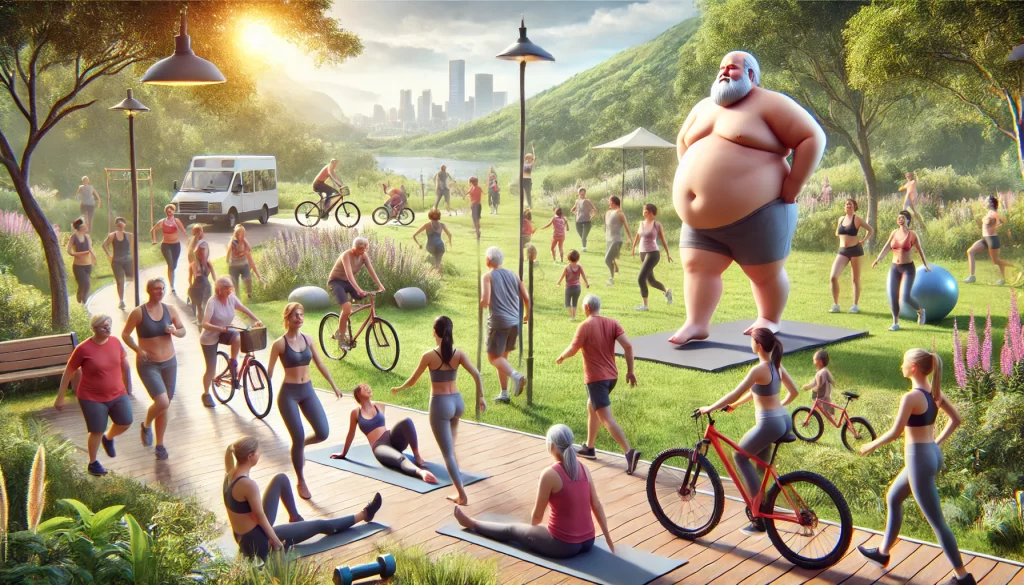

- Incorporate regular physical activities, including daily walking, yoga, aerobics, cycling, swimming, or any enjoyable physical exercise.
- Minimize sedentary time; take breaks to stretch or walk during long working hours.
- Limit screen time to reduce sedentary behaviour and improve sleep quality.
- Stress Management:

- Adopt stress-reducing practices such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness techniques.
- Engage in hobbies or recreational activities that promote relaxation and emotional well-being.
- Seek professional counseling if emotional eating or binge eating due to stress becomes a regular issue.
- Sleep Improvement:
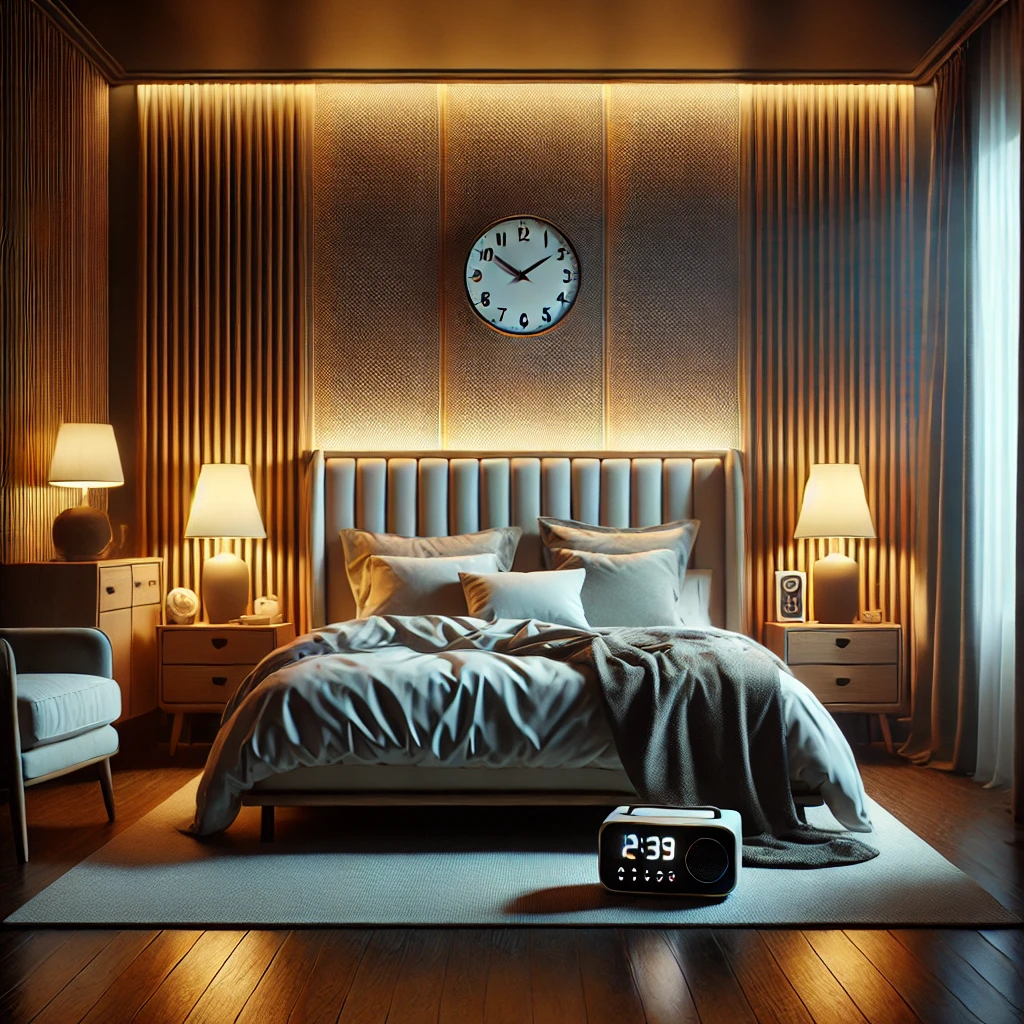

- Maintain consistent sleep schedules by sleeping and waking up at the same time daily.
- Create a conducive sleeping environment that is quiet, comfortable, and free from distractions like screens or bright lights.
- Limit caffeine and heavy meals close to bedtime to ensure uninterrupted sleep.
- Preventive Healthcare:
- Regular health check-ups to monitor weight, BMI, blood sugar, cholesterol, and other obesity-related markers.
- Consultation with nutritionists or dieticians for personalized diet plans and guidance.
- Awareness and education regarding the nutritional value and caloric content of common foods consumed regularly.

Conclusion: Prime Minister Modi’s alert on obesity should serve as a wake-up call for the nation. Addressing obesity effectively demands proactive changes at personal, family, and societal levels. By recognizing early signs, adjusting dietary habits, incorporating physical activities, managing stress, and improving sleep hygiene, Indians can significantly reduce the risk of obesity, leading to healthier, more productive lives.